Author Evaluation Indicators
Author Evaluation Indicators
Used to evaluate a researcher's academic influence. The calculation typically involves using the number of publications by the researcher and the number of times their papers have been cited, to fully present their research performance.
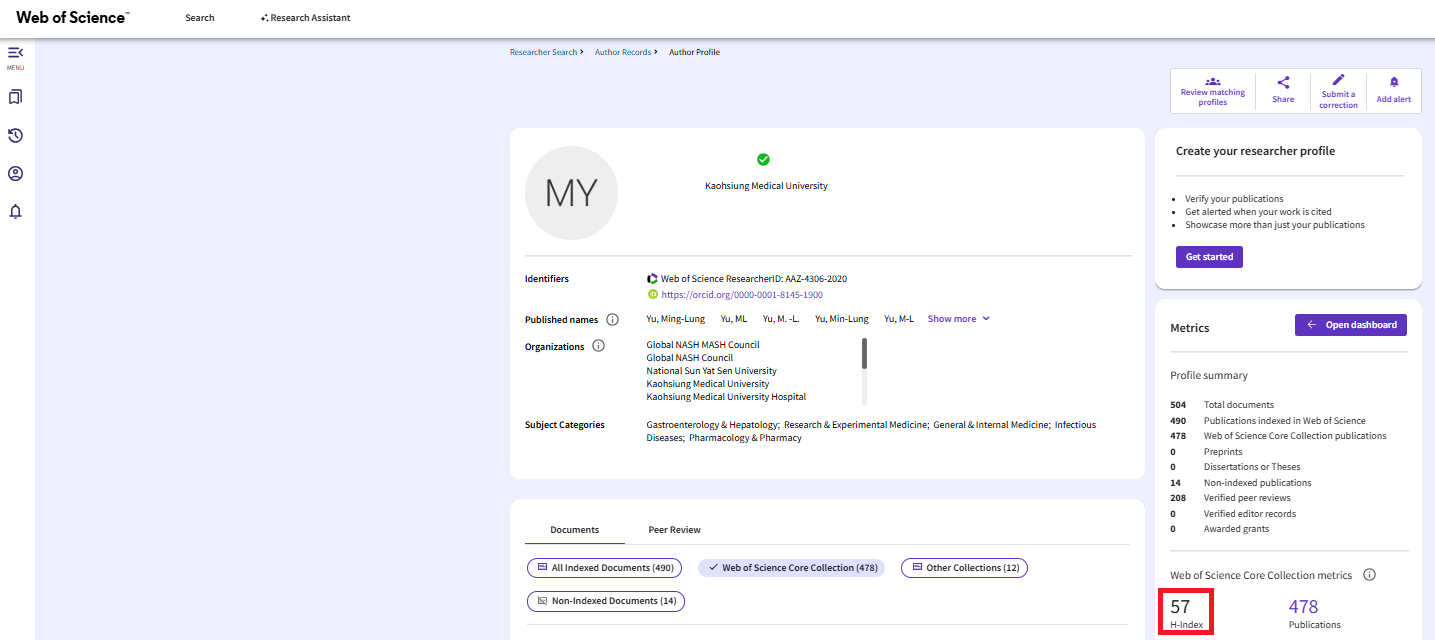
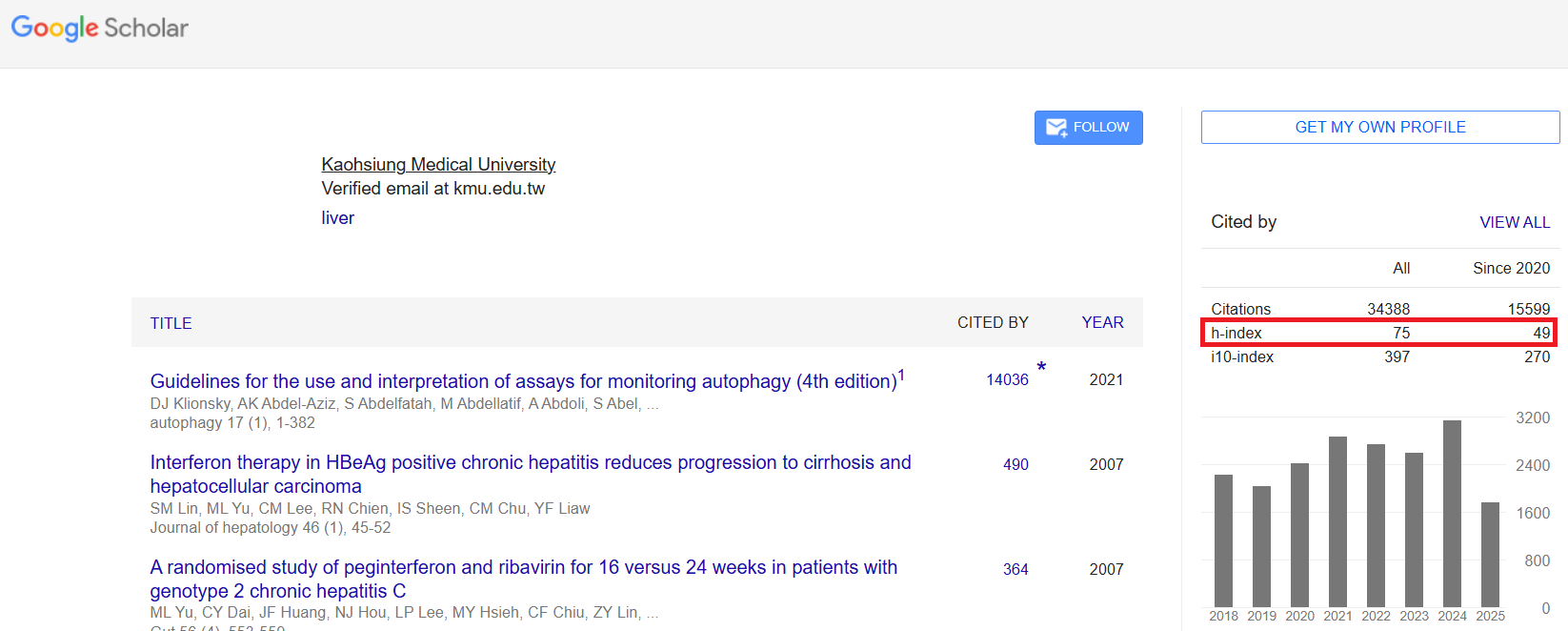
H-Index
The H-index is a statistical indicator proposed by scholar J.E. Hirsch in 2005. The H-index represents "h papers that have been cited at least h times." For example, if a researcher has 15 publications that have been cited at least 15 times, their H-index value is 15.
~Features and Limitations~Features and LimitationsFeatures and Limitations~
-
- The H-index simultaneously considers both the quality and quantity of papers, and eliminates the influence of extreme values, making it widely used in academia.
- This index is related to the number of publications and citations, which can be less favorable for younger researchers.
- Different academic fields have different citation patterns, making it less suitable for cross-disciplinary comparisons.
~Indicator Source Databases~
The following are subscription or free databases where the H-index can be queried. The H-index may vary because different databases have different coverage.
CNCI (Category Normalized Citation Impact)
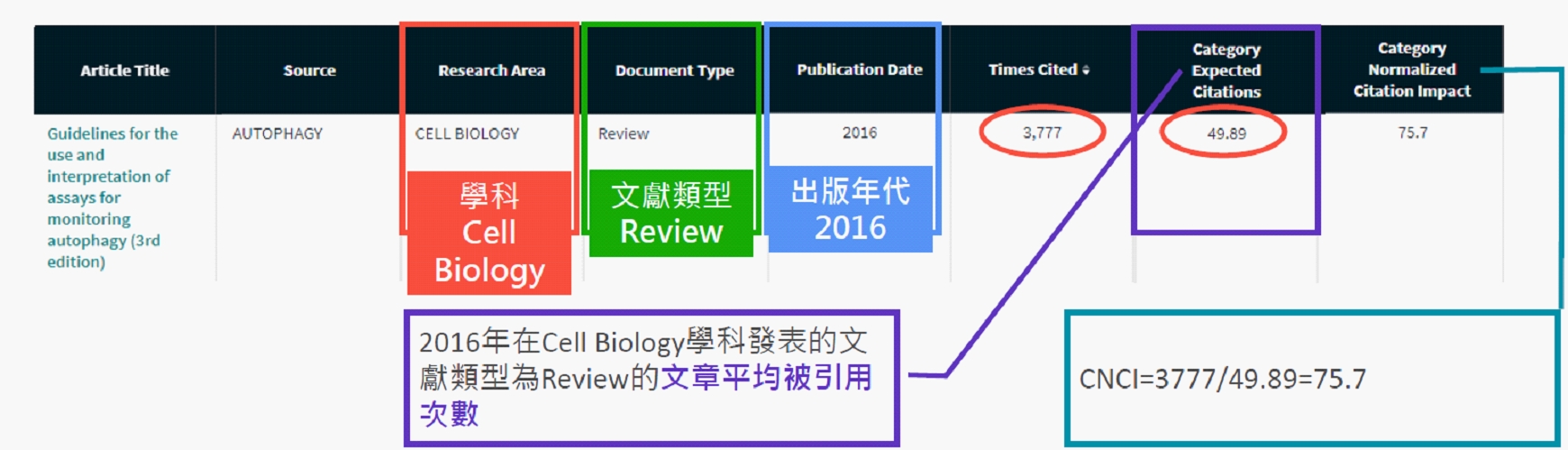
Category Normalized Citation Impact (CNCI) is a value obtained by dividing the number of times a paper has been cited by the average number of citations for papers of the same document type, publication year, and subject area. If the CNCI value is >1, it indicates that the citation impact of the researcher or paper is higher than the global average. If the CNCI value is <1, it indicates that the citation impact of the researcher or paper is lower than the global average.
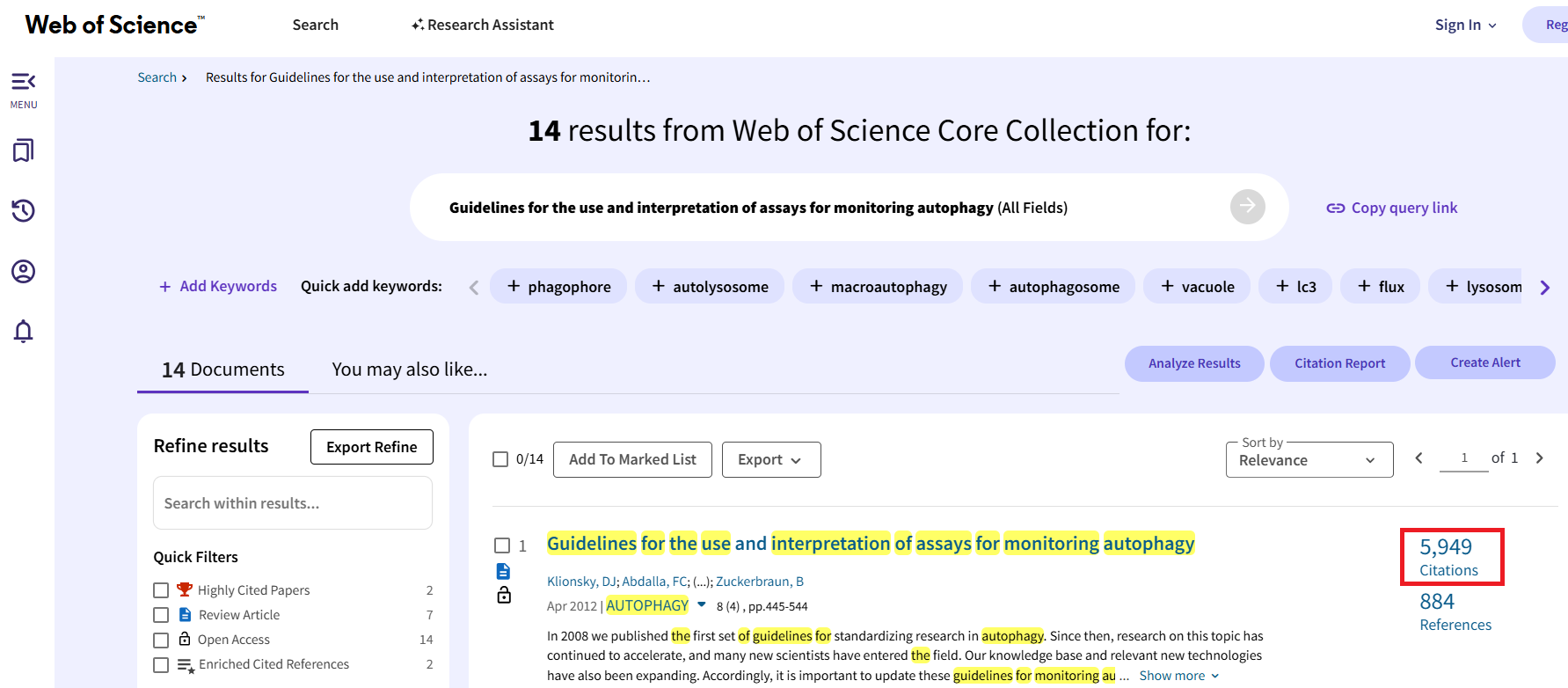
Taking the figure below as an example, the paper was cited 3,777 times, while the average number of citations in the same subject area (Cell Biology), same document type (Review), and same publication year (2016) was 49.89. The CNCI for this paper is 3777/49.89 = 75.7.
~Features and Limitations~
-
- CNCI eliminates the influence of publication year, subject area, and document type, providing a normalized indicator, thus allowing for cross-disciplinary comparisons.
- It can quickly review the "quality performance" or "impact performance" of papers published by researchers or institutions.
- The numerical calculation is based on papers in the WOS database; papers not indexed by WOS cannot be calculated.
~Indicator Source Databases~
Article Evaluation Indicators
Article Evaluation Indicators
In the past, article evaluation indicators were based on the number of times a paper was cited, thereby assessing the overall impact of the paper. However, with the rapid changes in academic communication channels and the booming development of academic social media, a combination of traditional and innovative article evaluation metrics (e.g., Altmetrics) has emerged.
Citation Count (Times Cited)
Refers to the number of times a paper has been cited by other academic papers since its public publication. Citation count is usually considered an indicator of a research paper's impact and importance.
~Indicator Source Databases~~指標
WOS
 來源料指標來源資料庫標資料庫~
來源料指標來源資料庫標資料庫~
Highly Cited Papers、Hot Papers
Based on SCIE and SSCI, highly cited papers are defined as the top 1% most cited papers in their respective fields within the last 10 years. Hot papers are defined as the top 0.1% most cited papers within the last 2 years.
~Indicator Source Databases~
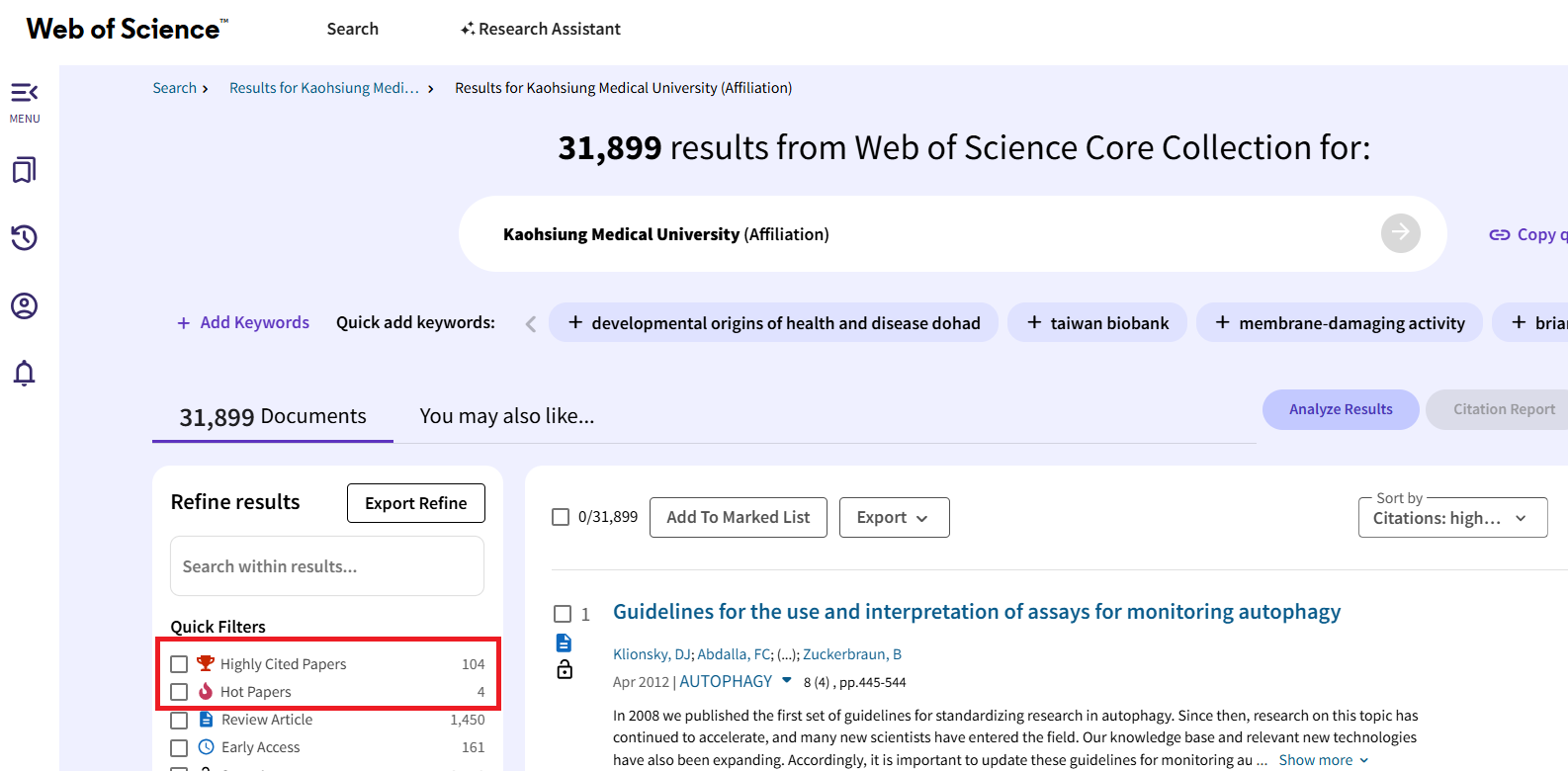
- WOS -The quick filter function on the left side of the search results will show "Highly Cited Papers" and "Hot Papers" for filtering (as shown in the figure below).
- Essential Science Indicators(ESI)
CNCI (Category Normalized Citation Impact)
CNCI, or Category Normalized Citation Impact, is simply a value obtained by dividing the number of times a paper has been cited by the average number of citations for papers of the same document type, publication year, and subject area. If the CNCI value is >1, it indicates that the citation impact of the researcher or paper is higher than the global average. If the CNCI value is <1, it indicates that the citation impact of the researcher or paper is lower than the global average.
Taking the figure below as an example, the paper was cited 3,777 times, while the average number of citations in the same subject area (Cell Biology), same document type (Review), and same publication year (2016) was 49.89. The CNCI for this paper is 3777/49.89 = 75.7.

~Features and Limitations~
-
- CNCI eliminates the influence of publication year, subject area, and document type, providing a normalized indicator, thus allowing for cross-disciplinary comparisons.
- It can quickly review the "quality performance" or "impact performance" of papers published by researchers or institutions.
- The numerical calculation is based on papers in the WOS database; papers not indexed by WOS cannot be calculated.
~Indicator Source Databases~

Journal Evaluation Indicators
Journal Evaluation Indicators
Used to assess a journal's influence and importance within a specific field. It can also help researchers identify predatory journals when submitting papers and serve as a basis for deciding which journal to submit to.
JIF(Journal Impact Factor)
Journal Impact Factor (IF or JIF) is an important indicator used by academia and researchers to measure the influence of academic journals. It is calculated by dividing the total number of times papers published by the journal in the previous two years were cited (A) by the total number of papers published by the journal in the previous two years (B). Thus, IF = A/B (as shown in the figure, using JAMA Surgery's 2023 IF value as an example).

~Features and Limitations~
-
- Journals from different academic fields cannot be compared with each other (science and medical journals typically have higher citation counts than humanities and social science journals).
- Impact Factor is an indicator for evaluating journal influence and does not apply to individual articles or authors. Therefore, it cannot be used to assess paper quality or author influence.
~Indicator Source Databases~
JCI(Journal Citation Indicator)
This indicator applies CNCI's normalized calculation data (excluding the influence of subject area, document type, and publication year), allowing for comparisons between interdisciplinary journals in related fields. For example, JAMA Surgery's 2023 JCI = 5.97 indicates that the journal's citation impact is 5.97 times higher than the global average.

~Indicator Source Databases~
JNCI(Journal Normalized Citation Impact)
Journal Normalized Citation Impact (JNCI) provides a normalized indicator by excluding the influence of document type and publication year. The JNCI for each paper is the ratio of that paper's citation count to the average citation count of papers of the same publication year and document type published in that journal. It primarily assesses how a paper performs within the journal it was published in. JNCI > 1 indicates that the paper's citation performance is higher than the global average, while JNCI < 1 indicates that the paper's citation performance is lower than the average citation performance of other papers in the same journal from the same period.
~Indicator Source Databases~







 來源料指標來源資料庫標資料庫~
來源料指標來源資料庫標資料庫~


